-40%
MICHAEL VII Ducas 1071AD JESUS CHRIST Follis LARGE Ancient Byzantine Coin i65104
$ 104.96
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
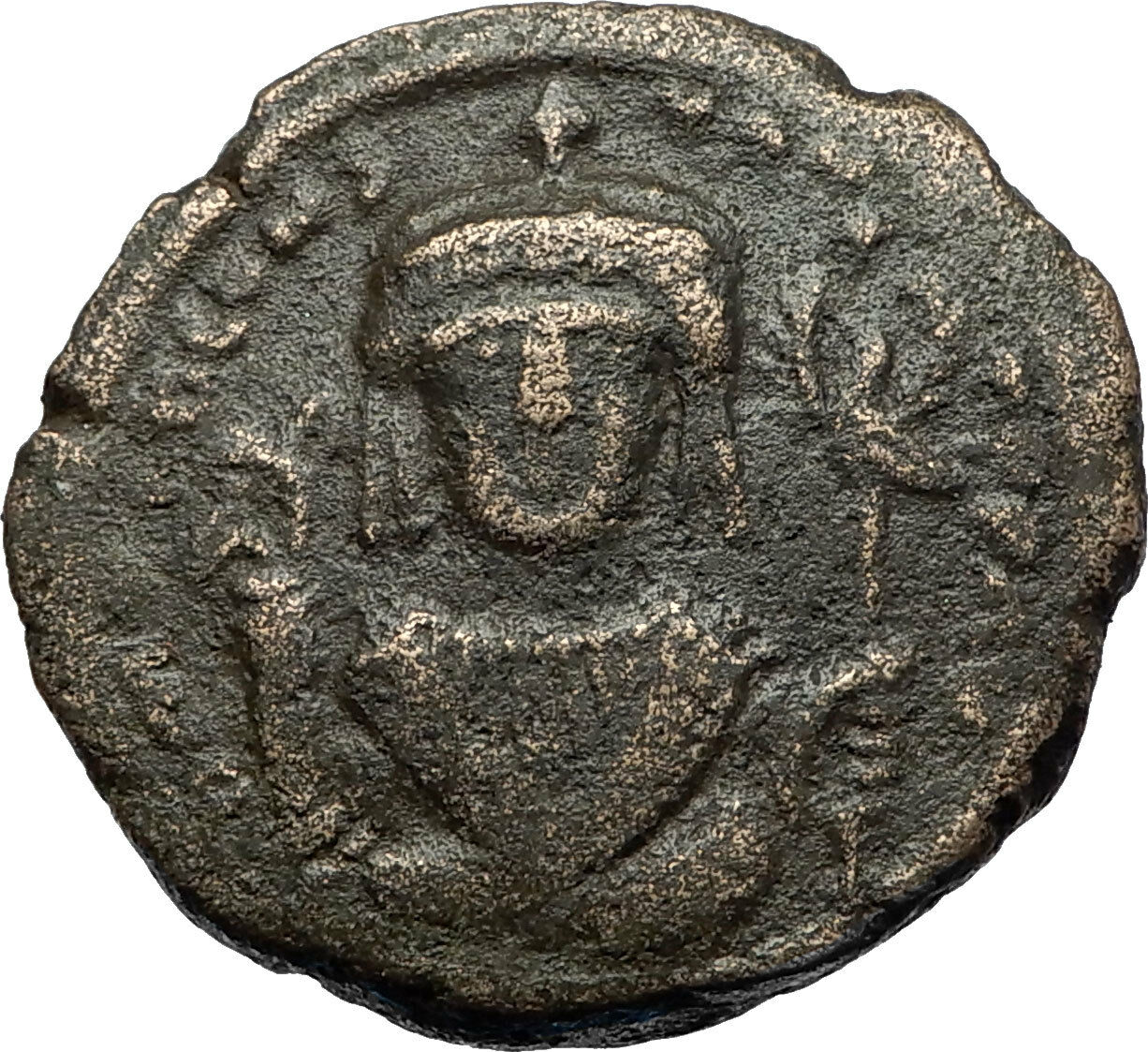
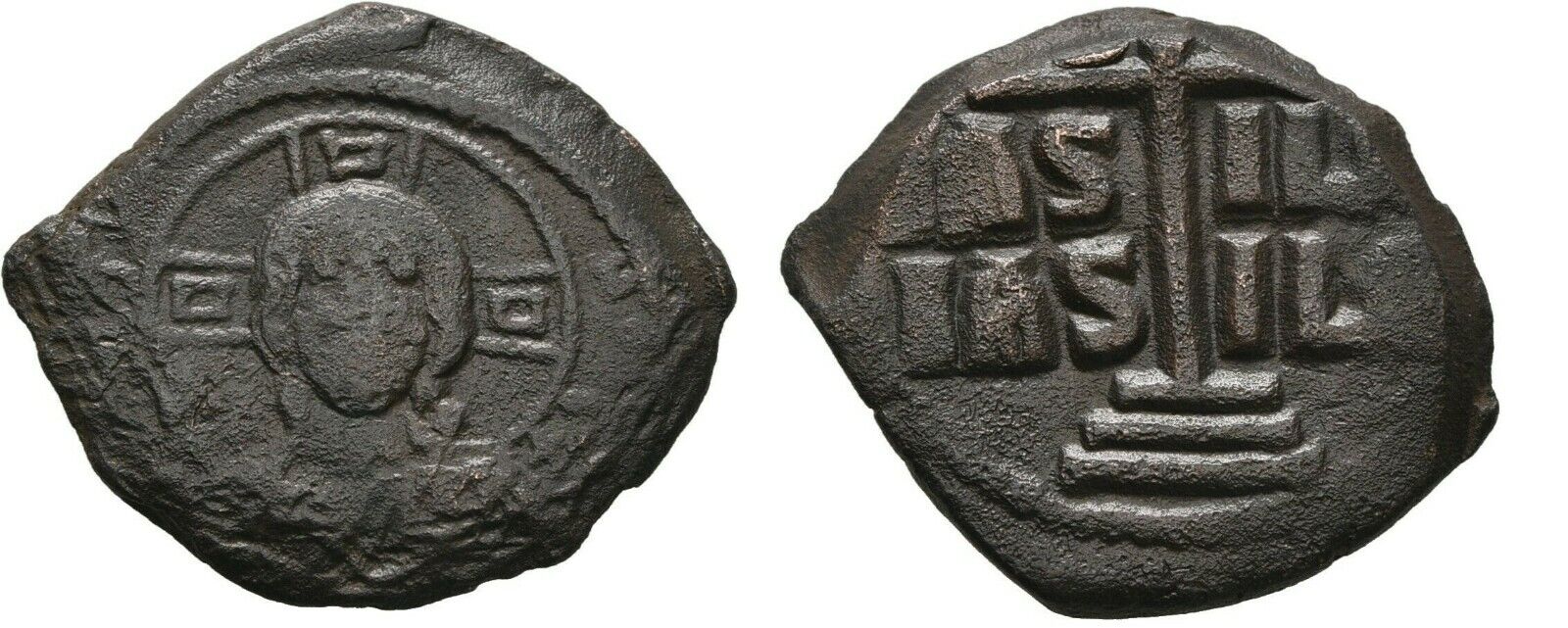
Item:i65104
Authentic Ancient Coin of:
Byzantine Empire
Michael VII, Ducas
- Emperor: October 24, 1071 A.D. - March 24, 1078 A.D.
Bronze Follis 27mm (7.78 grams) Constantinople mint: 1071-1078 A.D.
Reference:
Sear 1878
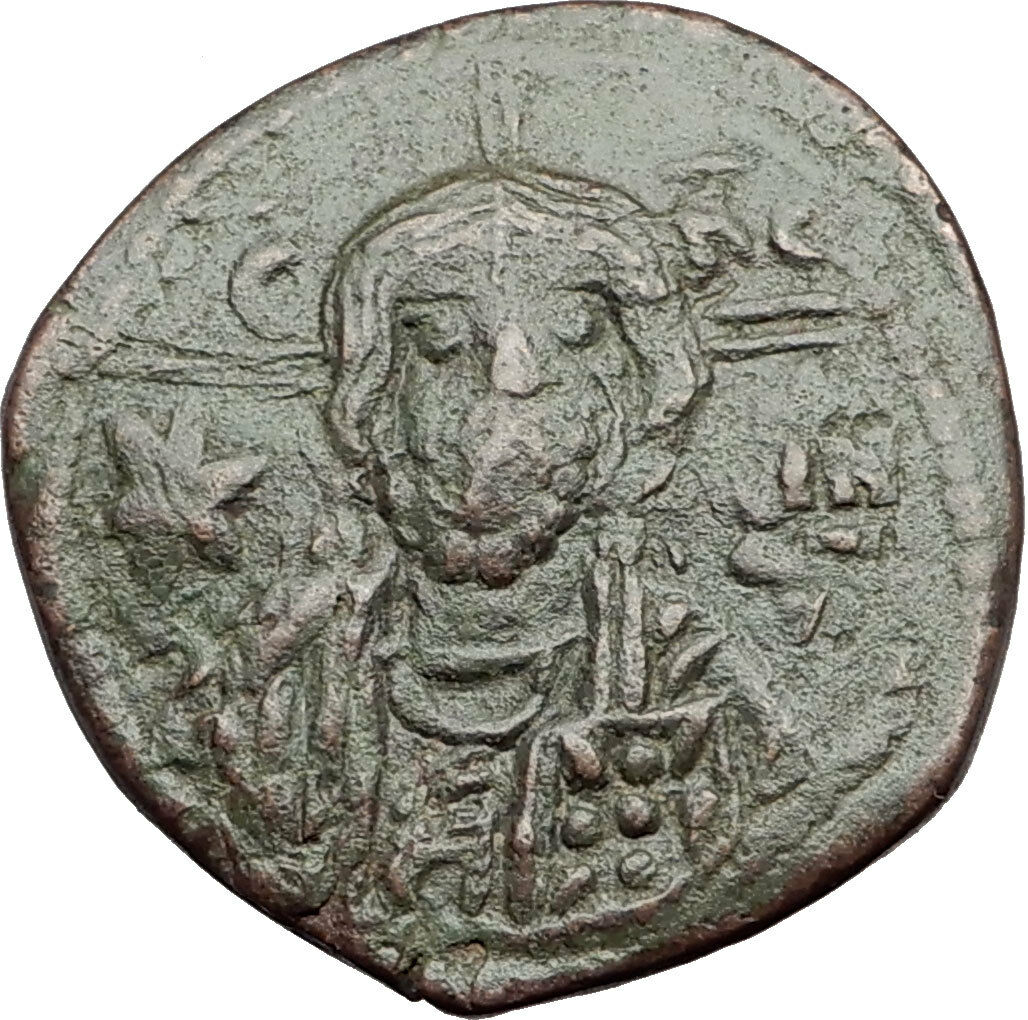
Bust of
Christ
facing, cross behind head, wearing pallium and colobium, and raising right hand in benediction; in left hand, book of Gospels; in field, above transverse limbs of cross, IC - XC; beneath limbs, large star on either side of bust.
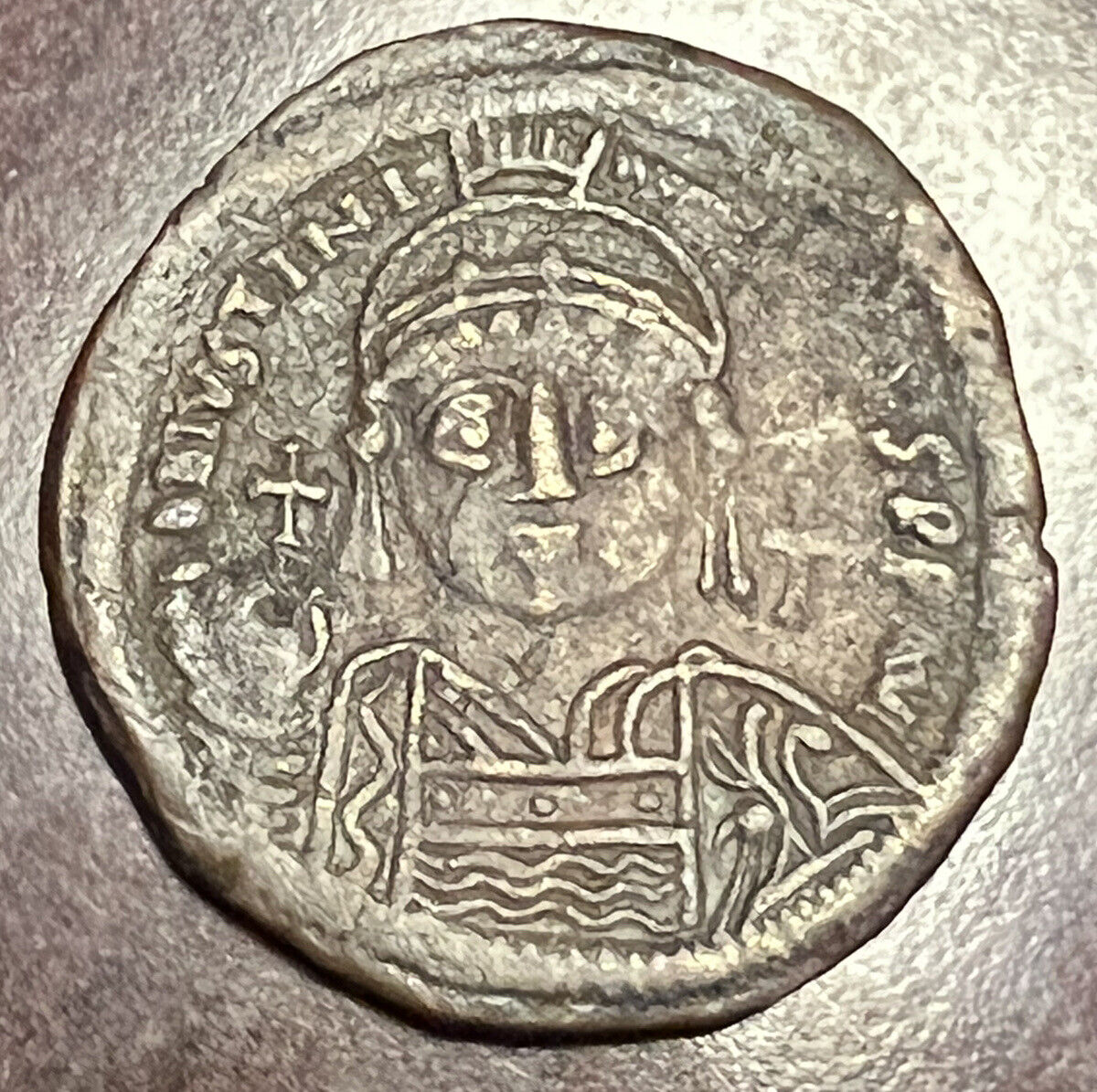
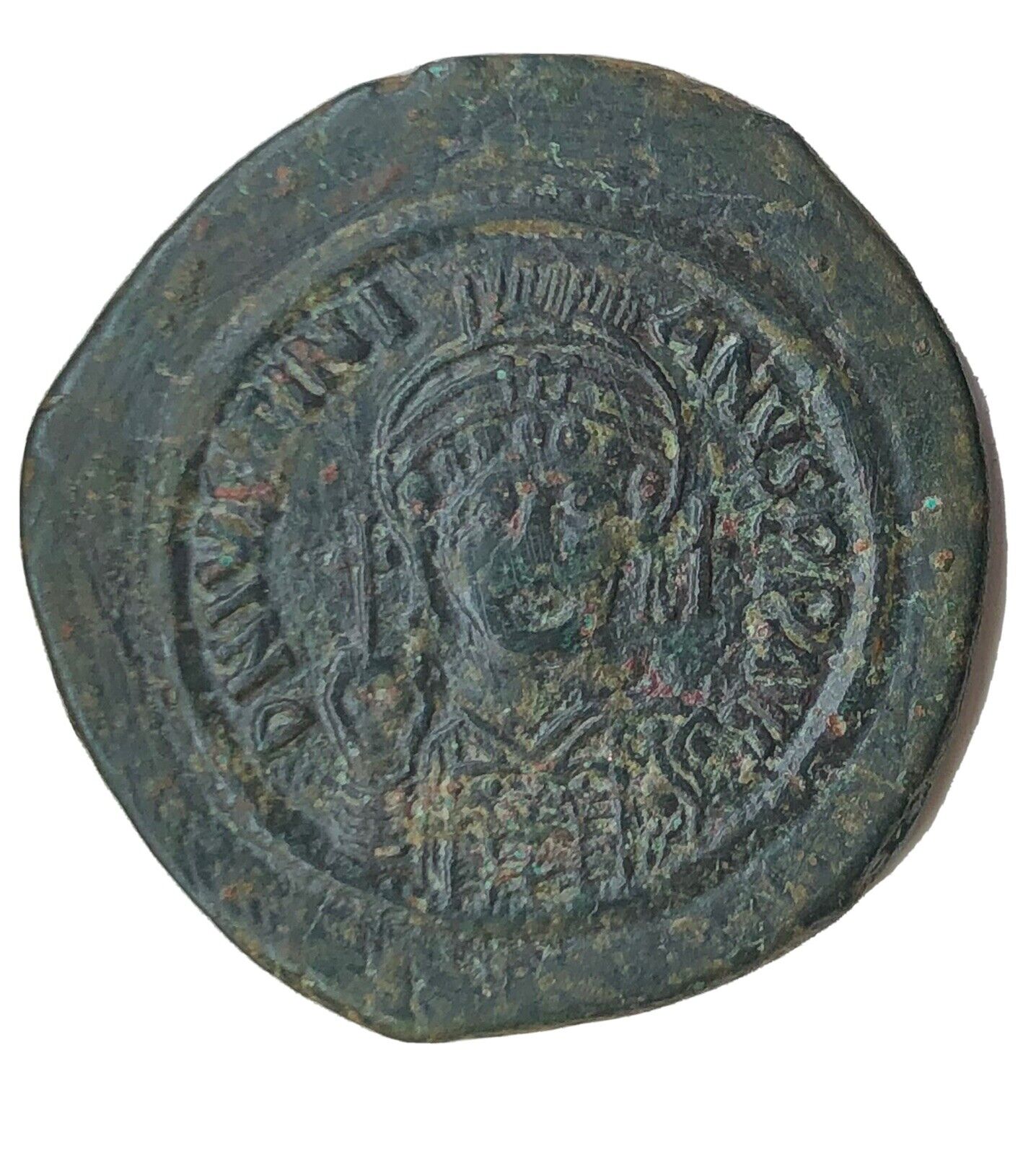
+ MIXAHΛ RACIΛ O Δ, Bust facing, bearded, wearing crown and loros, and holding
labarum
and globe cross.
For more than a century, the production of Follis denomination Byzantine coins had religious Christian motifs which included included Jesus Christ, and even Virgin Mary. These coins were designed to honor Christ and recognize the subservient role of the Byzantine emperor, with many of the reverse inscriptions translating to "Jesus Christ King of Kings" and "May Jesus Christ Conquer". The Follis denomination coins were the largest bronze denomination coins issued by the Byzantine empire, and their large size, along with the Christian motif make them a popular coin type for collectors. This series ran from the period of Byzantine emperors John I (969-976 A.D.) to Alexius I (1081-1118 A.D.). The accepted classification was originally devised by Miss Margaret Thompson with her study of these types of coins. World famous numismatic author, David R. Sear adopted this classification system for his book entitled, Byzantine Coins and Their Values. The references about this coin site Mr. Sear's book by the number that they appear in that work. The class types of coins included
Class A1
,
Class A2
,
Class B
,
Class C
,
Class D
,
Class E
,
Class F
,
Class G
,
Class H
,
Class I
,
Class J
,
Class K
. Read more and see examples of these coins by reading the
JESUS CHRIST Anonymous Class A-N Byzantine Follis Coins Reference
.
Click here to see all the Jesus Christ Anonymous Follis coins for sale.
Click here to see all coins bearing Jesus Christ or related available for sale.
You are bidding on the exact item pictured, provided with a Certificate of Authenticity and Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity.
Jesus
(7-2 BC to AD 30-33), also referred to as Jesus of Nazareth or Jesus Christ, is the central figure of Christianity, whom the teachings of most Christian denominations hold to be the Son of God. Christians believe Jesus is the awaited Messiah (or Christ, the Anointed One) of the Old Testament.
Virtually all modern scholars of antiquity agree that Jesus existed historically, and historians consider the Synoptic Gospels (Matthew, Mark and Luke) to be the best sources for investigating the historical Jesus. Most scholars agree that Jesus was a Galilean, Jewish rabbi who preached his message orally, was baptized by John the Baptist, and was crucified by the order of the Roman Prefect Pontius Pilate. In the current mainstream view, Jesus was an apocalyptic preacher and the founder of a renewal movement within Judaism, although some prominent scholars argue that he was not apocalyptic. After Jesus' death, his followers believed he was resurrected, and the community they formed eventually became the Christian church. The widely used calendar era, abbreviated as "AD" from the Latin "Anno Domini" ("in the year of our Lord") or sometimes as "CE", is based on the birth of Jesus.
Christians believe that Jesus has a "unique significance" in the world. Christian doctrines include the beliefs that Jesus was conceived by the Holy Spirit, was born of a virgin named Mary, performed miracles, founded the Church, died by crucifixion as a sacrifice to achieve atonement, rose from the dead, and ascended into Heaven, whence he will return. Most Christians believe Jesus enables humans to be reconciled to God, and will judge the dead either before or after their bodily resurrection, an event tied to the Second Coming of Jesus in Christian eschatology; though some believe Jesus's role as savior has more existential or societal concerns than the afterlife, and a few notable theologians have suggested that Jesus will bring about a universal reconciliation. The great majority of Christians worship Jesus as the incarnation of God the Son, the second of three persons of a Divine Trinity. A few Christian groups reject Trinitarianism, wholly or partly, as non-scriptural.
In Islam, Jesus (commonly transliterated as Isa) is considered one of God's important prophets and the Messiah, second in importance only to Muhammad. To Muslims, Jesus was a bringer of scripture and was born of a virgin, but was not the Son of God. According to the Quran, Jesus was not crucified but was physically raised into Heaven by God. Judaism rejects the belief that Jesus was the awaited Messiah, arguing that he did not fulfill the Messianic prophecies in the Tanakh.
In Christian iconography,
Christ Pantocrator
refers to a specific depiction of Christ.
Pantocrator
or
Pantokrator
(Greek: Χριστός Παντοκράτωρ) is, used in this context, a translation of one of many names of God in Judaism.
When the Hebrew Bible was translated into Greek as the Septuagint,
Pantokrator
was used both for
YHWH Sabaoth
"Lord of Hosts" and for
El Shaddai
"God Almighty." In the New Testament, Pantokrator is used once by Paul (2 Cor 6:18). Aside from that one occurrence, John of Patmos is the only New Testament author to use the word Pantokrator. The author of the Book of Revelation uses the word nine times, and while the references to God and Christ in Revelation are at times interchangeable, Pantokrator appears to be reserved for God except, perhaps, in 1:8.
Meaning
The most common translation of
Pantocrator
is "Almighty" or "All-powerful." In this understanding,
Pantokrator
is a compound word formed from the Greek words πᾶς,
pas
(GEN παντός
pantos
), i.e. "all" and κράτος,
kratos,
i.e. "strength," "might," "power." This is often understood in terms of potential power; i.e., ability to do anything, omnipotence.
Another, more literal translation is "Ruler of All" or, less literally, "Sustainer of the World". In this understanding, Pantokrator is a compound word formed from the Greek for "all" and the verb meaning "To accomplish something" or "to sustain something" (κρατεῖν,
kratein
). This translation speaks more to God's actual power; i.e., God does everything (as opposed to God can do everything).
The Pantokrator, largely an Eastern Orthodox or Eastern Catholic theological conception, is less common by that name in Western (Roman) Catholicism and largely unknown to most Protestants. In the West the equivalent image in art is known as Christ in Majesty, which developed a rather different iconography.
Christ Pantocrator
has come to suggest Christ as a mild but stern, all-powerful judge of humanity.
Iconography
The icon of Christ Pantokrator is one of the most widely used religious images of Orthodox Christianity. Generally speaking, in Medieval eastern roman church art and architecture, an iconic mosaic or fresco of Christ Pantokrator occupies the space in the central dome of the church, in the half-dome of the apse or on the nave vault. Some scholars (Latourette 1975: 572) consider the Pantocrator a Christian adaptation of images of Zeus, such as the great statue of Zeus enthroned at Olympia. The development of the earliest stages of the icon from Roman Imperial imagery is easier to trace.
The image of Christ Pantocrator was one of the first images of Christ developed in the Early Christian Church and remains a central icon of the Eastern Orthodox Church. In the half-length image, Christ holds the New Testament in his left hand and makes the gesture of teaching or of blessing with his right. The typical Western Christ in Majesty is a full-length icon that in the early Middle Ages usually showed Christ in a mandorla or other geometric frame, surrounded by the Four Evangelists or their symbols.
The oldest known surviving example of the icon of Christ Pantocrator was painted in encaustic on panel in the sixth or seventh century, and survived the period of destruction of images during the Iconoclastic disputes that twice racked the Eastern church, 726 to 787 and 814 to 842, by being preserved in the remote desert of the Sinai, in Saint Catherine's Monastery. The gessoed panel, finely painted using a wax medium on a wooden panel, had been coarsely overpainted around the face and hands at some time around the thirteenth century. It was only when the overpainting was cleaned in 1962 that the ancient image was revealed to be a very high quality icon, probably produced in Constantinople.
[
citation needed
]
The icon, traditionally half-length when in a semi-dome, which became adopted for panel icons also, depicts Christ fully frontal with a somewhat melancholy and stern aspect, with the right hand raised in blessing or, in the early encaustic panel at Saint Catherine's Monastery, the conventional rhetorical gesture that represents teaching. The left hand holds a closed book with a richly decorated cover featuring the Cross, representing the Gospels. An icon where Christ has an open book is called "Christ the Teacher", a variant of the Pantocrator. Christ is bearded, his brown hair centrally parted, and his head is surrounded by a halo. The icon is usually shown against a gold background comparable to the gilded grounds of mosaic depictions of the Christian emperors.
Often, the name of Christ is written on each side of the halo, as IC and XC. Christ's fingers are depicted in a pose that represents the letters IC, X and C, thereby making the Christogram
ICXC
(for "Jesus Christ"). The IC is composed of the Greek characters iota (Ι) and lunate sigma (C; instead of Σ, ς)-the first and last letters of 'Jesus' in Greek (Ἰησοῦς); in XC the letters are chi (Χ) and again the lunate sigma-the first and last letters of 'Christ' in Greek (Χριστός). You can see an example of the early pre-400 AD Greek "IC XC" shorthand by clicking | Here | and scrolling down to Matt. 1:16.
In many cases, Christ has a cruciform halo inscribed with the letters Ο Ω Ν, i.e. ὁ ὢν "He Who Is".
Michael VII Doukas
or
Dukas
/
Ducas
(Greek: Μιχαήλ Ζ΄ Δούκας,
Mikhaēl VII Doukas
), nicknamed
Parapinakēs
(Παραπινάκης), was Byzantine emperor from 1071 to 1078.
Life
Michael VII was born c. 1050 in Constantinople, the eldest son of Constantine X Doukas and Eudokia Makrembolitissa. He was associated with his father on the throne late in 1059, together with or shortly before his newly born brother Konstantios Doukas. When Constantine X died in 1067, Michael VII was 17 years old and should have been able to rule by himself. He exhibited little interest in politics, however, and his mother Eudokia and uncle John Doukas governed the empire as effective regents.
On January 1, 1068, Eudokia married the general Romanos Diogenes, who now became senior co-emperor alongside Michael VII, Konstantios, and another brother, Andronikos. When Romanos IV was defeated and captured by Alp Arslan of the Seljuk Turks at the Battle of Manzikert in August 1071, Michael VII remained in the background, while the initiative was taken by his uncle John Doukas and his tutor Michael Psellos. They conspired to keep Romanos from regaining power after his release from captivity, while Michael felt no obligation to honor the agreement that Romanos struck with the Sultan. After the dispatch of Eudokia to a monastery, Michael VII was crowned again on October 24, 1071 as senior emperor.
Although still advised by Michael Psellos and John Doukas, Michael VII became increasingly reliant on his finance minister Nikephoritzes. The emperor's chief interests, shaped by Psellos, were in academic pursuits, and he allowed Nikephoritzes to increase both taxation and luxury spending without properly financing the army. As an emperor he was incompetent, surrounded by sycophantic court officials, and blind to the empire collapsing around him. In dire straits, imperial officials resorted to property confiscations and even expropriated some of the wealth of the church. The underpaid army tended to mutiny, and the Byzantines lost Bari, their last possession in Italy, to the Normans of Robert Guiscard in 1071. Simultaneously, they faced a serious revolt in the Balkans, where they faced an attempt for the restoration of the Bulgarian state. Although this revolt was suppressed by the general Nikephoros Bryennios, the Byzantine Empire was unable to recover its losses in Asia Minor.
After Manzikert, the Byzantine government sent a new army to contain the Seljuk Turks under Isaac Komnenos, a brother of the future emperor Alexios I Komnenos, but this army was defeated and its commander captured in 1073. The problem was made worse by the desertion of the Byzantines' western mercenaries, who became the object of the next military expedition in the area, led by the
Caesar
John Doukas. This campaign also ended in failure, and its commander was likewise captured by the enemy. The victorious mercenaries now forced John Doukas to stand as pretender to the throne. The government of Michael VII was forced to recognize the conquests of the Seljuks in Asia Minor in 1074, and to seek their support. A new army under Alexios Komnenos, reinforced by Seljuk troops sent by Malik Shah I, finally defeated the mercenaries and captured John Doukas in 1074.
These misfortunes caused widespread dissatisfaction, exacerbated by the devaluation of the currency, which gave the emperor his nickname
Parapinakēs
, "minus a quarter". In 1078 two generals, Nikephoros Bryennios and Nikephoros Botaneiates, simultaneously revolted in the Balkans and Anatolia, respectively. Botaneiates gained the support of the Seljuk Turks, and he reached Constantinople first. Michael VII resigned the throne with hardly a struggle on March 31, 1078 and retired into the Monastery of Stoudios. He later became metropolitan of Ephesus and died in Constantinople in c. 1090.
Usurpers
Various usurpers attempted to overthrow Michael VII or rule parts of the empire. These included:
Nestor - A former slave of Constantine X, Nestor had been promoted to become the dux of Paradounavon, a region bordering the Danube. Having had much of his property and wealth confiscated by the minister Nikephoritzes, he rebelled in around 1076, placing himself at the head of the garrisons under his command, which were already in a state of mutiny due to an arrears in their pay. The troops were eager to plunder the Bulgarians, and Nestor obtained the assistance of one of the chiefs of the Patzinaks before marching onto Constantinople. The rebels demanded the dismissal of Nikephoritzes, but discovering that he didn't have the numbers to attack the capital, Nestor's troops separated into smaller parties and proceeded to plunder Thrace. Defeated by Alexios Komnenos in 1078, Nestor remained with the Patzinaks, and retreated with them back to Paradunavum.
Philaretos Brachamios
Caesar John Doukas
Nikephoros Bryennios
Nikephoros Botaneiates
Family
Michael VII Doukas married Maria of Alania, daughter of King Bagrat IV of Georgia. By her he had at least one son, Constantine Doukas, co-emperor from c. 1075 to 1078 and from 1081 to 1087/8. He died c. 1095.
Sources
Primary Sources
Michael Psellus,
Chronographia
.
Frequently Asked Questions
Mr. Ilya Zlobin
, world-renowned expert numismatist, enthusiast, author and dealer in authentic ancient Greek, ancient Roman, ancient Byzantine, world coins & more.
Who am I dealing with?
You are dealing with Ilya Zlobin, ancient coin expert, enthusiast, author and dealer with an online store having a selection of over 15,000 items with great positive feedback from verified buyers and over 10 years experience dealing with over 57,000 ancient and world coins and artifacts. Ilya Zlobin is an independent individual who has a passion for coin collecting, research and understanding the importance of the historical context and significance all coins and objects represent. Most others are only concerned with selling you, Ilya Zlobin is most interested in educating you on the subject, and providing the largest selection, most professional presentation and service for the best long-term value for collectors worldwide creating returning patrons sharing in the passion of ancient and world coin collecting for a lifetime.
How long until my order is shipped?
Orders are shipped by the next business day (after receipt of payment) most of the time.
How will I know when the order was shipped?
After your order has shipped, you will be left positive feedback, and that date could be used as a basis of estimating an arrival date. Any tracking number would be found under your 'Purchase history' tab.
USPS First Class mail takes about 3-5 business days to arrive in the U.S. International shipping times cannot be estimated as they vary from country to country.
Standard international mail to many countries
does not
include a tracking number, and can also be slow sometimes.
For a tracking number and signature confirmation, you may want to do Express Mail International Shipping, which costs more, however, is the fastest and most secure. Additionally you may be able to receive your order in as little as 3-5 business days using this method. For Express Mail International, it may be possible to place up to 10-15 items in one package (for the one shipping cost) as it is flat rate envelope, which may be the most cost-effective, secure and fastest way to receive items internationally. Send me a message about this and I can update your invoice should you want this method.
Getting your order to you, quickly and securely is a top priority and is taken seriously here.
Great care is taken in packaging and mailing every item securely and quickly.
Please be aware, I cannot take responsibility for any postal service delivery delays, especially for international packages as it may happen in rare instances.
What is a certificate of authenticity and what guarantees do you give that the item is authentic?
Each of the items sold here, is provided with a Certificate of Authenticity, and a Lifetime Guarantee of Authenticity, issued by a world-renowned numismatic and antique expert that has identified over 57,000 ancient coins and has provided them with the same guarantee. You will be very happy with what you get with the COA; a professional presentation of the coin, with all of the relevant information and a picture of the coin you saw in the listing. Additionally, the coin is inside it's own protective coin flip (holder), with a 2x2 inch description of the coin matching the individual number on the COA.
On the free-market such a presentation alone, can be considered a - value all in itself, and it comes standard with your purchases from me,
FREE.
With every purchase, you are leveraging my many years of experience to get a more complete context and understanding of the piece of history you are getting. Whether your goal is to collect or give the item as a gift, coins presented like this could be more prized and valued higher than items that were not given such care and attention to.
Buy a coin today and own a piece of history, guaranteed.
Is there a money back guarantee?
I offer a 30 day unconditional money back guarantee. I stand behind my coins and would be willing to exchange your order for either store credit towards other coins, or refund, minus shipping expenses, within 30 days from the receipt of your order. My goal is to have the returning customers for a lifetime, and I am so sure in my coins, their authenticity, numismatic value and beauty, I can offer such a guarantee.
When should I leave feedback?
Once you receive your order, please leave a positive feedback. Please don't leave any negative feedbacks, as it happens sometimes that people rush to leave feedback before letting sufficient time for their order to arrive. Also, if you sent an email, make sure to check for my reply in your messages before claiming that you didn't receive a response. The matter of fact is that any issues can be resolved, as reputation is most important to me. My goal is to provide superior products and quality of service.
How and where do I learn more about collecting ancient coins?
Visit the "
Guide on How to Use My Store
" for on an overview about using my store, with additional information and links to all other parts of my store which may include educational information on topics you are looking for.